Studentenprojekte
Generation of Physics-Based Synthetic Cerebrovascular 4D Flow MRI Data

Time-resolved volumetric phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (4D flow MRI) offers a non-invasive method to capture in-vivo blood flow patterns in the brain. However the accuracy and precision of the measurements cannot be quantified due to the lack of paired ground truth flow data with cerebrovascular MR measurements.
Schlagwörter
4D Flow MRI, computational fluid dynamics, modeling, blood flow, meshing
Labels
Semester Project
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-12-01 , Frühester Start: 2025-12-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-08-01
Bewerbungen eingeschränkt auf ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , University of Lausanne , University of Geneva , University of Zurich , University of St. Gallen , University of Lucerne , University of Fribourg , University of Berne , University of Basel
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Dirix Pietro
Themen Engineering and Technology
Evaluating nnU-Net Robustness for Aortic and Ventricular Segmentation in heavily undersampled 3D Radial PC-bSSFP

This project evaluates how pretrained nnU-Net models perform when input images are progressively degraded to mimic the undersampling and artifacts of 3D radial PC-bSSFP, determining up to what degradation level reliable aortic and ventricular segmentation—and resulting physiological parameters—can still be obtained.
Schlagwörter
3D radial PC-bSSFP, Segmentation, nnU-Net, Deep learning, Aortic flow, Undersampling simulation
Labels
Semester Project
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-12-01 , Frühester Start: 2026-03-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-09-30
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Malich Jacob
Themen Engineering and Technology
Using (Pre-)Balancing Gradients in 3D Radial PC-bSSFP to extract Multi-Echo Water–Fat Separated Images

This project investigates whether half-echo signals generated by pre-/rephasing gradients in 3D radial PC-bSSFP can be exploited to obtain multi-echo data for water–fat separation.
Schlagwörter
Water–fat imaging, 3D radial PC-bSSFP, Multi-echo MRI, IDEAL, 4D Flow MRI, Low-field MRI, MAP Image reconstruction, Half-echo acquisitions
Labels
Semester Project
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-12-01 , Frühester Start: 2026-03-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-11-30
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Malich Jacob
Themen Engineering and Technology
Learning Based Estimation of Pulse Wave Velocity from Noisy Low Resolution Data

Aortic pulse wave velocity (PWV) is a key biomarker of cardiovascular health. It can be estimated using phase-contrast (PC) MRI, with both data-driven and physics-informed neural networks, but the accuracy of these methods needs to be validated against ground truth.
Schlagwörter
reduced-order modelling, neural networks, aortic flow, pulse wave velocity, vessel compliance, physics-informed
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-11-28 , Frühester Start: 2025-12-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-09-01
Bewerbungen eingeschränkt auf ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , University of Basel , University of Berne , University of Fribourg , University of Geneva , University of Lausanne , University of Lucerne , University of St. Gallen , University of Zurich
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Dirix Pietro
Themen Engineering and Technology
Comparing bSSFP and GRE cine MRI for automated aortic segmentation using deep learning

The aim of this project is to quantitatively compare two image sequences commonly used in cardiac MRI by employing automated segmentation based on convolutional neural networks.
Schlagwörter
Aortic segmentation, Cardiac MRI, Deep learning, Swiss Heart Study, Medical image analysis
Labels
Semester Project
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-11-17 , Frühester Start: 2025-12-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-06-30
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Wolkerstorfer Gloria
Themen Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Quantification of myocardial blood perfusion from cardiac perfusion MRI using physics-informed neural networks (PINN)

Ischemia is a less-than-normal amount of blood flow to part of your body. It can happen particularly in heart and brain which causes severe life-threatening conditions. However, most of the current imaging technics only provides qualitative assessment, resulting in uncertainty in determining the severity of the disease. This study focuses on assessment of ischemia in heart muscles (myocardium) using cardiac perfusion magnetic resonance imaging (Perfusion MRI) and physics-informed neural networks (PINN) to quantify the level of perfusion in different locations of myocardium.
Schlagwörter
Image quantification, physics-informed neural networks (PINN), cardiac MRI
Labels
Semester Project
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-11-05 , Frühester Start: 2026-03-01 , Spätestes Ende: 2026-11-30
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Yan Chang
Themen Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
In-silico cardiac and cardiovascular modelling with physics informed neural networks
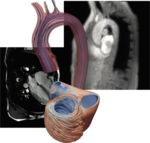
The aim of the project is to investigate the benefits, requirements and drawbacks of physics informed neural networks in the context of personalised cardiac and cardiovascular models
Schlagwörter
cardiac modelling, neural network, in-silico models, personalized medicine, reduced-order modelling, fluid dynamics, continuum mechanics, aortic flow
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-11-04 , Frühester Start: 2020-09-01
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Buoso Stefano , Kozerke Sebastian, Prof
Themen Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Digital twinning with physics-informed graph neural networks
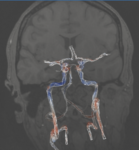
The aim of this project is to develop an approach based on physics-based graph neural networks to generate digital twins from PC-MRI data.
Schlagwörter
Physics informed neural networks, graph neural networks, digital twins, blood flow, brain, circulatory system, AI, biophysical
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
Mehr Informationen
Dieses Projekt öffnen... call_made
Publiziert seit: 2025-11-04 , Frühester Start: 2025-11-01
Organisation(en) Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Host(s) Buoso Stefano , Kozerke Sebastian, Prof
Themen Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology